Alfred Kastler
Alfred Kastler | |
|---|---|
 Alfred Kastler in 1966 | |
| Born | (1902-05-03)3 May 1902 Guebwiller, Alsace, German Empire |
| Died | 7 January 1984 (aged 81) Bandol, France |
| Nationality | French |
| Alma mater | École Normale Supérieure, University of Paris[1] |
| Known for | Optical pumping Nuclear acoustic resonance |
| Awards | Holweck Prize (1954) CNRS Gold medal (1964) Nobel Prize for Physics (1966) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | physics |
| Doctoral advisor | Pierre Daure [fr] |
| Doctoral students | Claude Cohen Tannoudji |
Alfred Kastler (French: [kastlɛʁ]; 3 May 1902 – 7 January 1984) was a French physicist, and Nobel Prize laureate.[2] He is known for the development of optical pumping.
Biography
Kastler was born in Guebwiller (Alsace, German Empire) and later attended the Lycée Bartholdi in Colmar, Alsace, and École Normale Supérieure in Paris in 1921. After his studies, in 1926 he began teaching physics at the Lycée of Mulhouse, and then taught at the University of Bordeaux, where he was a university professor until 1941. Georges Bruhat asked him to come back to the École Normale Supérieure, where he finally obtained a chair in 1952.
Collaborating with Jean Brossel, he researched quantum mechanics, the interaction between light and atoms, and spectroscopy. Kastler, working on combination of optical resonance and magnetic resonance, developed the technique of "optical pumping". Those works led to the completion of the theory of lasers and masers.
He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1966 "for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying Hertzian resonances in atoms".
He was president of the board of the Institut d'optique théorique et appliquée and served as the first chairman of the non-governmental organization (NGO) Action Against Hunger.
Kastler also wrote poetry (in German). In 1971 he published Europe, ma patrie: Deutsche Lieder eines französischen Europäers (i.e. Europe, my fatherland: German songs of a French European).
In 1976, Kastler was elected to the American Philosophical Society.[3]
In 1978 he became foreign member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.[4]
In 1979, Kastler was awarded the Wilhelm Exner Medal.[5]
Laboratoire Kastler-Brossel
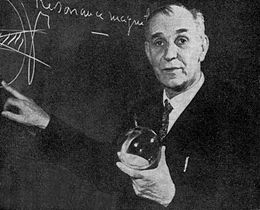
Professor Kastler spent most of his research career at the Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris where he started after the war with his student, Jean Brossel a small research group on spectroscopy.
Over the forty years that followed, this group has trained many of young physicists and had a significant impact on the development of the science of atomic physics in France. The Laboratoire de Spectroscopie hertzienne has then been renamed Laboratoire Kastler-Brossel in 1994 and has got a part of its laboratory in Université Pierre et Marie Curie mainly at the École Normale Supérieure.
Global policy
He was one of the signatories of the agreement to convene a convention for drafting a world constitution.[6][7] As a result, for the first time in human history, a World Constituent Assembly convened to draft and adopt the Constitution for the Federation of Earth.[8]
Death
Professor Kastler died on 7 January 1984, in Bandol, France.[9]
See also
Notes
- ^ At the time, the ENS was part of the University of Paris according to the decree of 10 November 1903.
- ^ Happer, William (May 1984). "Obituary: Alfred Kastler". Physics Today. 37 (5): 101–102. Bibcode:1984PhT....37e.101H. doi:10.1063/1.2916219.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "APS Member History". search.amphilsoc.org. Retrieved 2022-07-25.
- ^ "A.H.F. Kastler (1902 - 1984)". Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ^ Editor, ÖGV. (2015). Wilhelm Exner Medal. Austrian Trade Association. ÖGV. Austria.
- ^ "Letters from Thane Read asking Helen Keller to sign the World Constitution for world peace. 1961". Helen Keller Archive. American Foundation for the Blind. Retrieved 2023-07-01.
- ^ "Letter from World Constitution Coordinating Committee to Helen, enclosing current materials". Helen Keller Archive. American Foundation for the Blind. Retrieved 2023-07-03.
- ^ "Preparing earth constitution | Global Strategies & Solutions | The Encyclopedia of World Problems". The Encyclopedia of World Problems | Union of International Associations (UIA). Retrieved 2023-07-15.
- ^ Sullivan, Walter (8 January 1984). "Dr. Alfred Kastler, 81, Nobel Prize-Winner, Dies". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-11-06.
References
- Nobelstiftelsen (1972). Nobel Lectures, Physics 1963–1970. Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company. ISBN 0-444-40993-9.
- Kastler A (October 1967). "Optical Methods for Studying Hertzian Resonances". Science. 158 (3798): 214–221. Bibcode:1967Sci...158..214K. doi:10.1126/science.158.3798.214. PMID 17839496.
- Kastler A (July 1950). "Applications of polarimetry to infra-red and micro-wave spectroscopy". Nature. 166 (4211): 113. Bibcode:1950Natur.166..113K. doi:10.1038/166113a0. PMID 15439165. S2CID 4192600.
External links
- Alfred Kastler on Nobelprize.org
 including the Nobel Lecture, December 12, 1966 Optical Methods for Studying Hertzian Resonances
including the Nobel Lecture, December 12, 1966 Optical Methods for Studying Hertzian Resonances - Alfred Kastler biography at Timeline of Nobel Winners
- Alfred Kastler at the Mathematics Genealogy Project

- v
- t
- e
- 1901: Röntgen
- 1902: Lorentz / Zeeman
- 1903: Becquerel / P. Curie / M. Curie
- 1904: Rayleigh
- 1905: Lenard
- 1906: J. J. Thomson
- 1907: Michelson
- 1908: Lippmann
- 1909: Marconi / Braun
- 1910: Van der Waals
- 1911: Wien
- 1912: Dalén
- 1913: Kamerlingh Onnes
- 1914: Laue
- 1915: W. L. Bragg / W. H. Bragg
- 1916
- 1917: Barkla
- 1918: Planck
- 1919: Stark
- 1920: Guillaume
- 1921: Einstein
- 1922: N. Bohr
- 1923: Millikan
- 1924: M. Siegbahn
- 1925: Franck / Hertz
- 1926: Perrin
- 1927: Compton / C. Wilson
- 1928: O. Richardson
- 1929: De Broglie
- 1930: Raman
- 1931
- 1932: Heisenberg
- 1933: Schrödinger / Dirac
- 1934
- 1935: Chadwick
- 1936: Hess / C. D. Anderson
- 1937: Davisson / G. P. Thomson
- 1938: Fermi
- 1939: Lawrence
- 1940
- 1941
- 1942
- 1943: Stern
- 1944: Rabi
- 1945: Pauli
- 1946: Bridgman
- 1947: Appleton
- 1948: Blackett
- 1949: Yukawa
- 1950: Powell
- 1951: Cockcroft / Walton
- 1952: Bloch / Purcell
- 1953: Zernike
- 1954: Born / Bothe
- 1955: Lamb / Kusch
- 1956: Shockley / Bardeen / Brattain
- 1957: C. N. Yang / T. D. Lee
- 1958: Cherenkov / Frank / Tamm
- 1959: Segrè / Chamberlain
- 1960: Glaser
- 1961: Hofstadter / Mössbauer
- 1962: Landau
- 1963: Wigner / Goeppert Mayer / Jensen
- 1964: Townes / Basov / Prokhorov
- 1965: Tomonaga / Schwinger / Feynman
- 1966: Kastler
- 1967: Bethe
- 1968: Alvarez
- 1969: Gell-Mann
- 1970: Alfvén / Néel
- 1971: Gabor
- 1972: Bardeen / Cooper / Schrieffer
- 1973: Esaki / Giaever / Josephson
- 1974: Ryle / Hewish
- 1975: A. Bohr / Mottelson / Rainwater
- 1976: Richter / Ting
- 1977: P. W. Anderson / Mott / Van Vleck
- 1978: Kapitsa / Penzias / R. Wilson
- 1979: Glashow / Salam / Weinberg
- 1980: Cronin / Fitch
- 1981: Bloembergen / Schawlow / K. Siegbahn
- 1982: K. Wilson
- 1983: Chandrasekhar / Fowler
- 1984: Rubbia / Van der Meer
- 1985: von Klitzing
- 1986: Ruska / Binnig / Rohrer
- 1987: Bednorz / Müller
- 1988: Lederman / Schwartz / Steinberger
- 1989: Ramsey / Dehmelt / Paul
- 1990: Friedman / Kendall / R. Taylor
- 1991: de Gennes
- 1992: Charpak
- 1993: Hulse / J. Taylor
- 1994: Brockhouse / Shull
- 1995: Perl / Reines
- 1996: D. Lee / Osheroff / R. Richardson
- 1997: Chu / Cohen-Tannoudji / Phillips
- 1998: Laughlin / Störmer / Tsui
- 1999: 't Hooft / Veltman
- 2000: Alferov / Kroemer / Kilby
present
- 2001: Cornell / Ketterle / Wieman
- 2002: Davis / Koshiba / Giacconi
- 2003: Abrikosov / Ginzburg / Leggett
- 2004: Gross / Politzer / Wilczek
- 2005: Glauber / Hall / Hänsch
- 2006: Mather / Smoot
- 2007: Fert / Grünberg
- 2008: Nambu / Kobayashi / Maskawa
- 2009: Kao / Boyle / Smith
- 2010: Geim / Novoselov
- 2011: Perlmutter / Schmidt / Riess
- 2012: Wineland / Haroche
- 2013: Englert / Higgs
- 2014: Akasaki / Amano / Nakamura
- 2015: Kajita / McDonald
- 2016: Thouless / Haldane / Kosterlitz
- 2017: Weiss / Barish / Thorne
- 2018: Ashkin / Mourou / Strickland
- 2019: Peebles / Mayor / Queloz
- 2020: Penrose / Genzel / Ghez
- 2021: Parisi / Hasselmann / Manabe
- 2022: Aspect / Clauser / Zeilinger
- 2023: Agostini / Krausz / L'Huillier