Ammonium cyanide
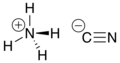 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | NH4CN |
| Molar mass | 44.0559 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.02 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 36 °C (decomp.) |
Solubility in water | very soluble |
| Solubility | very soluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure | cubic |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Ammonium hydroxide Ammonium azide Ammonium nitrate |
Other cations | Sodium cyanide Potassium cyanide |
Related compounds | Ammonia Hydrogen cyanide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Ammonium cyanide is an unstable inorganic compound with the formula NH4CN.
Uses
Ammonium cyanide is generally used in organic synthesis.[citation needed] Being unstable, it is not shipped or sold commercially.
Preparation
Ammonium cyanide is prepared by combining solutions of hydrogen cyanide and ammonia:[citation needed]
- HCN + NH3 → NH4CN
It may be prepared by the reaction of calcium cyanide and ammonium carbonate:[citation needed]
- Ca(CN)2 + (NH4)2CO3 → 2 NH4CN + CaCO3
In dry state, ammonium cyanide is made by heating a mixture of potassium cyanide or potassium ferrocyanide with ammonium chloride and condensing the vapours into ammonium cyanide crystals:[citation needed]
- KCN + NH4Cl → NH4CN + KCl
Reactions
Ammonium cyanide decomposes to ammonia and hydrogen cyanide, often forming a black polymer of hydrogen cyanide:[1]
- NH4CN → NH3 + HCN
It undergoes salt metathesis reaction in solution with a number of metal salts to form metal–cyanide complexes.
Reaction with ketones and aldehydes yield aminonitriles, as in the first step of the Strecker amino acid synthesis:
- NH4CN + CH3COCH3 → (CH3)2C(NH2)CN + H2O
Toxicity
Ammonium cyanide is highly toxic.
Notes
- ^ Matthews, Clifford N (1991). "Hydrogen cyanide polymerization: A preferred cosmochemical pathway". Bioastronomy: The Search for Extraterrestrial Life—The Exploration Broadens. Lecture Notes in Physics. Vol. 390. pp. 85–87. doi:10.1007/3-540-54752-5_195. ISBN 978-3-540-54752-5.
References
- A. F. Wells, Structural Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1984.
- v
- t
- e
| monatomic anions |
|
|---|---|
| oxyanions |
|
| other anions |
|
- Aluminon
- Ammonium acetate
- Ammonium adipate
- Ammonium benzoate
- Ammonium bituminosulfonate
- Ammonium carbamate
- Ammonium citrate
- Ammonium diethyl dithiophosphate
- Ammonium ferric citrate
- Ammonium formate
- Ammonium fumarate
- Ammonium glutamate
- Ammonium lactate
- Ammonium lauryl sulfate
- Ammonium malate
- Ammonium nonanoate
- Ammonium oxalate
- Ammonium picrate
- Ammonium perfluorononanoate
- Ammonium propionate
- Ammonium thioglycolate
- Cupferron
- Ferric ammonium oxalate
- Murexide











