Antrodemus
| Antrodemus Temporal range: Late Jurassic, 150 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ | |
|---|---|
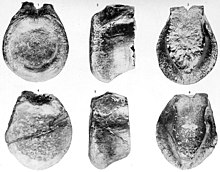 | |
| Holotype tail vertebra (above) compared to same of Allosaurus (below) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Allosauridae |
| Genus: | †Antrodemus Leidy, 1870 |
| Species: | †A. valens |
| Binomial name | |
| †Antrodemus valens (Leidy, 1870) Leidy, 1873 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Antrodemus ("chamber bodied") is a dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic, probably the Morrison Formation, of Middle Park, Colorado. It contains one species, Antrodemus valens, first described and named as a species of Poekilopleuron by Joseph Leidy in 1870.

Discovery and species

The first described fossil specimen was a bone obtained secondhand by Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden in 1869 (original discoverer unknown). It came from Middle Park, near Granby, Colorado, probably from Morrison Formation rocks. Hayden reported that several similar fossils had been identified as petrified horse hooves.[1] Hayden sent his specimen to Joseph Leidy, who identified it as half of a tail vertebra, and tentatively assigned it to the European dinosaur genus Poekilopleuron as Poicilopleuron [sic] valens, based on the shared presence of a large medullary cavity. He identified the presence of trabeculae in P. valens as a distinguishing character from P. bucklandii but also noted that should better remains show more characters that could sufficiently distinguish the two taxa, it might be named Antrodemus.[1] In 1873, he amended his description and identified the species as Antrodemus valens.[2]
In 1920, Charles W. Gilmore concluded that the tail vertebra named Antrodemus by Leidy was indistinguishable from those of Allosaurus and that Antrodemus should be the preferred name because, as the older name, it had priority.[3] Antrodemus became the accepted name for this familiar genus for over fifty years until James Madsen published on the Cleveland-Lloyd specimens of Allosaurus and concluded that the Allosaurus name should be used because Antrodemus was based on material with poor, if any, diagnostic features and locality information (for example, the geological formation that the single bone of Antrodemus came from is unknown).[4] Subsequent authors have agreed with this assessment and have considered Antrodemus a nomen dubium.[5][6]
References
- ^ a b Leidy, Joseph (1870). "Remarks on Poicilopleuron valens, Clidastes intermedius, Leiodon proriger, Baptemys wyomingensis, and Emys stevensonianus". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 22: 3–4.
- ^ Leidy, Joseph (1873). "Contribution to the extinct vertebrate fauna of the western territories". Report of the U.S. Geological Survey of the Territories I: 14–358.
- ^ Gilmore, Charles W. (1920). "Osteology of the carnivorous dinosauria in the United States National Museum, with special reference to the genera Antrodemus (Allosaurus) and Ceratosaurus". Bulletin of the United States National Museum (110): 1–159. doi:10.5479/si.03629236.110.i. hdl:2027/uiug.30112032536010.
- ^ Madsen, James H. Jr. (1993) [1976]. Allosaurus fragilis: A Revised Osteology. Utah Geological Survey Bulletin 109 (2nd ed.). Salt Lake City: Utah Geological Survey.
- ^ Paul, Gregory S.; Carpenter, Kenneth (2010). "Case 3506: Allosaurus Marsh, 1877 (Dinosauria, Theropoda): proposed conservation of usage by designation of a neotype for its type species Allosaurus fragilis Marsh, 1877" (PDF). The Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature. 67 (1): 53–56. doi:10.21805/bzn.v67i1.a7. S2CID 81735811.
- ^ Rauhut, Oliver W. M. (2011). "Theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic of Tendaguru (Tanzania)". Special Papers in Palaeontology. 86: 195–239.
External links
- "Theropoda: Avetheropoda: Allosauridae". Palaeos. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023.
- v
- t
- e
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
|   | |||||||||||||||||||
|     | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|  
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





















