Fecalith
Medical condition
| Fecalith | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Fecolith, coprolith, stercolith |
 | |
| A fecalith marked by the arrow which has resulted in acute appendicitis. | |
| Specialty | General surgery |
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is sometimes concurrent with appendicitis.[1] They can also obstruct diverticula. It can form secondary to fecal impaction. A fecaloma is a more severe form of fecal impaction, and a hardened fecaloma may be considered a giant fecalith. The term is from the Greek líthos=stone.[2]
Diagnosis
- CT scan
- Projectional radiography
- Ultrasound
Complications
A small fecalith is one cause of both appendicitis and acute diverticulitis.
-
 Appendicolith as seen on CT
Appendicolith as seen on CT -
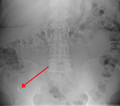 Appendicolith as seen on plain X ray
Appendicolith as seen on plain X ray
See also
- Bezoar
- Fecal impaction, including fecaloma
- Coprolith is also used to mean geologically fossilized feces.
References
- ^ Al-Nakshabandi, Nizar; Aljefri, Ahmad (2009). "The stranded stone: Relationship between acute appendicitis and appendicolith". Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. 15 (4): 258–60. doi:10.4103/1319-3767.56106. PMC 2981843. PMID 19794272.
- ^ Alaedeen, Diya I.; Cook, Marc; Chwals, Walter J. (May 2008). "Appendiceal fecalith is associated with early perforation in pediatric patients". Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 43 (5): 889–92. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.12.034. PMID 18485960.
External links
- Ramdass, Michael; Young, Quillan; Milne, David; Mooteeram, Justin; Barrow, Shaheeba (1 February 2015). "Association between the appendix and the fecalith in adults". Canadian Journal of Surgery. 58 (1): 10–14. doi:10.1503/cjs.002014. PMC 4309758. PMID 25427333.
- Nigar, Sofia; Sunkara, Tagore; Culliford, Andrea; Gaduputi, Vinaya (28 February 2017). "Giant Fecalith Causing Near Intestinal Obstruction and Rectal Ischemia". Case Reports in Gastroenterology. 11 (1): 59–63. doi:10.1159/000455186. PMC 5465791. PMID 28611554.
- Mahida, Justin B.; Lodwick, Daniel L.; Nacion, Kristine M.; Sulkowski, Jason P.; Leonhart, Karen L.; Cooper, Jennifer N.; Ambeba, Erica J.; Deans, Katherine J.; Minneci, Peter C. (June 2016). "High failure rate of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis with an appendicolith in children". Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 51 (6): 908–911. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.02.056. PMID 27018085.
- v
- t
- e
Diseases of the human digestive system
| Esophagus |
|
|---|---|
| Stomach |
Enteropathy
| Small intestine (Duodenum/Jejunum/Ileum) | |
|---|---|
| Large intestine (Appendix/Colon) | |
| Large and/or small |
|
| Rectum | |
| Anal canal |
| Liver | |
|---|---|
| Gallbladder | |
| Bile duct/ Other biliary tree | |
| Pancreatic |
| Hernia | |
|---|---|
| Peritoneal |












