Gapicomine
- none
- off market (was used in EU countries)
- 1-Pyridin-4-yl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)methanamine
- 1539-39-5
 Y
Y
- 68955
- 62178
 N
N
- WWW0P95393
- ChEMBL2103958
 N
N
- DTXSID10165477

- Interactive image
- n1ccc(cc1)CNCc2ccncc2
- InChI=1S/C12H13N3/c1-5-13-6-2-11(1)9-15-10-12-3-7-14-8-4-12/h1-8,15H,9-10H2
 N
N - Key:AUQQZPGNRKTPSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
 N
N
 N
N Y (what is this?) (verify)
Y (what is this?) (verify)Gapicomine (INN) is a coronary vasodilator. It has been withdrawn from the market in the countries it was used in.[1]
Also, gapicomine is a major component in the drug Bicordin.[2]
History
Gapicomine was discovered in 1970 by Polish chemist Stanisław Biniecki. It was first published about in an article of The Polish Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy describing the derivative drug Bicordin in 1974.[3]
Synthesis
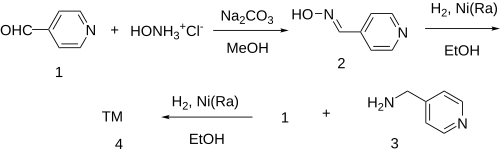
The oxime formation between isonicotinaldehyde [872-85-5] (1) and hydroxylamine gives 4-Pyridinealdoxime [696-54-8] (2). This is then reduced by catalytic hydrogenation over Raney-Nickel into 4-Picolylamine [3731-53-1] (3). Reductive amination of the last with a second equivalent of isonicotinaldehyde affords gapicomine (4).
References
- ^ "Gapicomine Monograph, The Index Nominum". Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ "Bicordin, PubChem". Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ Samochowiec L, Wójcicki J, Gregorczyk K, Szmatloch E (1974). "Bicordin--a new drug in the treatment of coronary heart disease". Mater Med Pol. 6 (4): 298–300. PMID 4453155.
- ^ Anon., GB 1058356 (1967 to Starogardzkie Zakl Farma).
- v
- t
- e
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
 | This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e









