Kovachevsko kale
- View a machine-translated version of the Bulgarian article.
- Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
- Consider adding a topic to this template: there are already 280 articles in the main category, and specifying
|topic=will aid in categorization. - Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
- You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is
Content in this edit is translated from the existing Bulgarian Wikipedia article at [[:bg:Ковачевско кале]]; see its history for attribution. - You may also add the template
{{Translated|bg|Ковачевско кале}}to the talk page. - For more guidance, see Wikipedia:Translation.

 Bulgaria
Bulgaria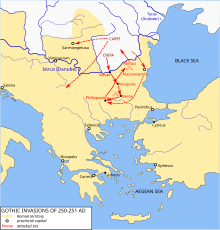
Kovachevsko kale (Bulgarian: Ковачевско кале) was a Roman city which lies 6 kilometres (4 mi) west of the Bulgarian town of Popovo. The Czech archaeologist Karel Škorpil called it Kovachoveshko kale, after the name of the nearby village, Kovachevets (at that time Kovachovets).
It is notable for its massive defensive walls which have a roughly triangular plan and enclosed an area of more than 40 hectares (app. 10 acres). The stone walls are fortified with 17 U-shaped towers. There are two gates, one to the west and one to the north-east.
The city is located on a flat terrain, naturally protected by rivers.
The strong 3.20 m thick walls were built between 308 and 324 AD during the joint reign of Roman Emperors Constantine I the Great and Licinius after the Gothic Wars of 250-269. The city was set on fire in the Second Gothic War of 376-382 AD. It was slowly restored until the invasion of Attila the Hun around 447 AD. Finally it was destroyed by the Slavs and Avars in the 580s.
Recent excavations by Veliko Tarnovo University “St. Cyril and St. Methodius" have revealed a huge Roman building from the 4th century AD within the walls which appears to have been a horreum (i.e. a granary).[1] It measured over 60m x 25m, though it has not been fully exposed. It had a massive double door of 2.4m width. The walls of the building are 1.3m wide reinforced with external buttresses. It had two stories and a basement and was constructed with opus mixtum. The granary was plundered and set on fire around 378 AD probably by the Goths.
An underground aqueduct built of clay pipes supplied the fortress with drinking water, descending from the northwest over several kilometres from Kalakoch hill.
-

-

-

-
 Undeciphered Latin inscription discovered outside the northern wall.
Undeciphered Latin inscription discovered outside the northern wall.
References
- ^ Archaeology in Bulgaria: http://archaeologyinbulgaria.com/2015/12/10/archaeologists-discover-huge-ancient-roman-horreum-granary-in-kovachevsko-kale-fortress-near-bulgarias-popovo/
External links
- Kovatchevsko kale - a 3D reconstruction by Marhis Architectural Studio
- Bulgarian castles - Kovachevsko kale (in Bulgarian)
- v
- t
- e
- Anevo Fortress
- Asen's Fortress
- Baba Vida
- Belogradchik Fortress
- Bozhenishki Urvich
- Byalgrad
- Castra Martis
- Castra ad Montanesium
- Cherven
- Devingrad
- Gate of Trajan
- Hisarlaka
- Kaliakra
- Kipilovo Fortress
- Kovachevsko kale
- Krasen
- Ktenia
- Lardea
- Lovech Fortress
- Lyutitsa
- Markeli
- Matochina Fortress
- Mezek Fortress
- Monyak
- Palace of Omurtag
- Patmos
- Perperikon
- Shumen Fortress
- Sostra
- Storgosia
- Trapezitsa
- Tsarevets
- Tsepina
- Urvich
- Ustra
- Vishegrad

 | This Ancient Rome–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This Byzantine Empire–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
















