Western spotted skunk
| Western spotted skunk[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Spilogale gracilis | |
 | |
| Spilogale gracilis amphialus | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mephitidae |
| Genus: | Spilogale |
| Species: | S. gracilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Spilogale gracilis (Merriam, 1890) | |
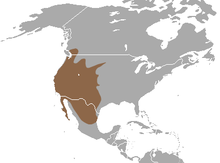 | |
Western spotted skunk range | |
The western spotted skunk (Spilogale gracilis) is a spotted skunk of western North America.
Description
With a total length of 35–45 cm (14–18 in), the western spotted skunk is smaller than the striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis). Males, which weigh 336 to 734 g (11.9 to 25.9 oz), are significantly heavier than females, at 227 to 482 g (8.0 to 17.0 oz), but only about 6% longer, on average. The adult is boldly striped black and creamy white, with three longitudinal stripes on each side of the front part of the body, and three vertical stripes on the hind-parts. One pair of longitudinal stripes runs either side of the spine, with the second pair running over the shoulders, and extending forward onto the face. The third pair is lower over the shoulders, and curves downward at the middle of the body to form the first pair of vertical stripes. Behind this, the second pair of vertical stripes rise from the knees to the rump, while the final stripes are often little more than spots.[3] In special cases, the normally black areas of the fur can appear in shades of red or brown, and areas of the skunk that traditionally appear white may appear in shades of gray or yellow, it is still unclear as to what causes the variation in color.[4]
The ears are short and rounded, while the face is marked with a white spot between the eyes, and a white patch below each ear. The animal has a conspicuously large, long-haired tail, measuring 10 to 16 cm (3.9 to 6.3 in). The hair on the tail is mostly black, but is white at the tip, and sometimes also on the upper surface. The claws on the fore-feet are longer, and more curved, than those on the hind feet.[3] The western spotted skunk's unique black and white pattern of spots and stripes and its small size differentiate them from regular striped skunks.[5]
As with other related species, western spotted skunks possess a pair of large musk glands that open just inside the anus, and which can spray their contents through muscular action. The musk is similar to that of striped skunks, but contains 2-phenylethanethiol as an additional component, and lacks some of the compounds produced by the other species. These differences are said to give western spotted skunk musk a more pungent odor, but not to spread as widely as that of striped skunks.[3]
Distribution and habitat

The western spotted skunk is found throughout the western United States, northern Mexico, and southwestern British Columbia in Canada. Their habitat is mixed woodlands, open areas, and farmlands. Their preferred areas of occupation differ greatly depending on what resources are available in the immediate area. In areas such as Idaho and Washington, they prefer riparian areas that have brush thickets in which to hide and forage. In contrast, members of the species that live in areas such as eastern Oregon or northern Mexico can often be found near cliffs and canyons.[6]
Behavior and diet
Western spotted skunks are nocturnal omnivores, feeding on insects, scorpions, small vertebrates, (such as mice, voles, other rodents, rabbit kits, small birds, small reptiles and amphibians), roots, grains, fruit, and berries.[7] Common insects eaten include beetles, grasshoppers, and caterpillars.[8] However, they have been found to consume prey as large as the ashy storm petrel. They also feed on eggs and carrion.[9] Populations close to these animals often have decreased pest populations. They have even been reported to consume scorpions in the southwest.[10]
Golden eagles are among their few predators. They spend the day in dens, and are usually solitary, although sometimes two or three females will share a single burrow.[3] Males remain solitary during the winter.[11]
Western spotted skunks will attempt to build reserves of fat before winter. While they do not engage in true hibernation, they may sleep for several weeks during the winter.[12] During this time, females may den in groups that have been observed as large as 20.[11]
When threatened, western spotted skunks display threat behavior, stamping their fore-feet before raising their hind parts in the air and showing their conspicuous warning coloration. While they can spray by standing on their forelegs and raising their hindlegs and tail in the air, they more commonly do so with all four feet on the ground, bending their body around so that both their head and their tail face the attacker.[3][13]
Reproduction
The western spotted skunk typically reaches sexual maturity faster than other skunk species.[7] Western spotted skunks typically mate in September when females come into heat, although both sexes remain fertile for several months thereafter if they fail to breed early.[14][5] After fertilization, the embryo develops to the blastocyst stage, but then becomes dormant for several months before implanting in the uterine wall around April. Including this period of delayed implantation, gestation lasts 230 to 250 days,[15] with the litter of two to five young being born in May.[14] These baby skunks are called kits.[5] At birth, the young are blind and almost hairless, weighing around 11 g (0.39 oz).[16] At around 4 or 5 months of age, young females become sexually mature and the cycle starts again.[5] Western spotted skunks have lived for almost ten years in captivity.[17]
Taxonomy and etymology
The western spotted skunk was first described by Clinton Hart Merriam in 1890;[18] its specific name, gracilis, is derived from the Latin for "slender".[3] There remains discussion on whether the western spotted skunk is a subspecies of the eastern spotted skunk (S. putorius), a common skunk in the eastern United States. Many support the idea that the two species are more distinctly evolved because of contrasts in morphology, breeding strategy, and molecular data.[19][14] There are currently seven recognized subspecies of S. gracilis that are indigenous to the western United States and northern Mexico, which were discovered in the late 1800s and early 1900s by biologists Merriam and Elliot.[20] The different subspecies reside in select locations within the western spotted skunk territory and therefore are acclimated to specific climates and niches in these areas.
Subspecies
Seven subspecies are generally recognized:[1]
- S. g. amphialus Dickey, 1929 — Channel Islands spotted skunk (Channel Islands of California)
- S. g. gracilis Merriam, 1890 — from south-eastern Washington to the extreme west of Oklahoma
- S. g. latifrons Merriam, 1890 — southwestern British Columbia to western Oregon
- S. g. leucoparia Merriam, 1890 — southern Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas, and northern Mexico
- S. g. lucasana Merriam, 1890 — southern Baja California
- S. g. martirensis Elliot, 1903 — northern and central Baja California
- S. g. phenax Merriam, 1890 — California
Interaction with humans
Skunks are increasingly kept as house pets and can be trained to use a litter box much like a house cat (Felis catus).[citation needed] S. gracilis can cause problems in rural areas, as it will make dens on private property and in the attics of homes, and has a tendency to steal eggs from farmers.[10] The western spotted skunk is one of many species that are opportunistic within the expansion of human civilization, and remains neither endangered nor threatened.[7]
References
- ^ a b Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 623. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Cuarón, A.D.; Helgen, K.; Reid, F. (2016). "Spilogale gracilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136797A45221721. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136797A45221721.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Verts, B.J.; Carraway, L.N. & Kinlaw, A. (2001). "Spilogale gracilis". Mammalian Species. 674: Number 674: pp. 1–10. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2001)674<0001:SG>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 5999413.
- ^ Carraway, L. N., Verts, B. J., & Kinlaw, A. (2001). Spilogale gracilis. Mammalian Species. doi: 10.2307/0.674.1
- ^ a b c d Webmaster, David Ratz. "Western Spotted Skunk - Montana Field Guide". fieldguide.mt.gov. Retrieved 2020-11-25.
- ^ Carey, A. B., & Kershner, J. E. (1996). Spilogale gracilis in Upland Forests of Western Washington and Oregon. Northwestern Naturalist, 77(2), 29. doi: 10.2307/3536615
- ^ a b c Hakkinen, K. (2001). "Spilogale gracilis" (On-line), Animal diversity web. Accessed October 13, 2019 at https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Spilogale_gracilis/
- ^ Baker, R.H. & Baker, M.W. (1975). "Montane habitat used by the spotted skunk (Spilogale putorius) in Mexico". Journal of Mammalogy. 56 (3): 671–673. doi:10.2307/1379480. JSTOR 1379480.
- ^ Mciver, W. R., Carter, H. R., Harvey, A. L., Mazurkiewicz, D. M., Howard, J. A., Martin, P. L., & Mason, J. W. (2018). Avian and Skunk Predation of Ashy Storm-Petrels at Santa Cruz Island, California. Western North American Naturalist, 78(3), 421–440. doi: 10.3398/064.078.0313
- ^ a b Davis, W., Schmidly. (1994). The Mammals of Texas. Austin, TX: Texas parks and wildlife nongame and urban program.
- ^ a b University of Nebraska-Lincoln. (1977). Plains Anthropologist, 22(75), 84–84. doi: 10.1080/2052546.1977.11908814
- ^ Genoways, H. H. (1984). Jones, J. K., Jr., D. M. Armstrong, R. S. Hoffmann, and C. Jones. MAMMALS OF THE NORTHERN GREAT PLAINS. Univ. Nebraska Press, Lincoln, xii 379 pp., illustrated, 1983. Price, $32.50 (hardbound). Journal of Mammalogy, 65(4), 730–731. doi: 10.2307/1380869
- ^ Crooks, K.R. & Van Vuren, D. (1995). "Resource utilization by two insular endemic mammalian carnivores, the island fox and island spotted skunk". Oecologia. 104 (3): 301–307. Bibcode:1995Oecol.104..301C. doi:10.1007/BF00328365. PMID 28307586. S2CID 11431727.
- ^ a b c Mead, R.A. (1968). "Reproduction in western forms of the spotted skunk (genus Spilogale)". Journal of Mammalogy. 49 (3): 373–390. doi:10.2307/1378196. JSTOR 1378196. PMID 5691422.
- ^ Foreman, K.R. & Mead, R.A. (1973). "Duration of post-implantation in a western subspecies of the spotted skunk (Spilogale putorius)". Journal of Mammalogy. 54 (2): 521–523. doi:10.2307/1379146. JSTOR 1379146. PMID 4706258.
- ^ Constantine, D.G. (1968). "Gestation period in the spotted skunk". Journal of Mammalogy. 42 (3): 421–422. doi:10.2307/1377064. JSTOR 1377064.
- ^ Egoscue, H.J.; Bittmein, J.G. & Petrovich, J.A. (1970). "Some fecundity and longevity records for captive small mammals". Journal of Mammalogy. 51 (3): 622–623. doi:10.2307/1378407. JSTOR 1378407.
- ^ ITIS Report. "ITIS Standard Report: Spilogale gracilis". Retrieved December 8, 2007.
- ^ Mead, R. A. (1968) [full citation needed]
- ^ Schmid, R., Wilson, D. E., & Reeder, D. M. (1993). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. Taxon, 42(2), 512. doi: 10.2307/1223169
External links
 Media related to Spilogale gracilis at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Spilogale gracilis at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Spilogale at Wikispecies
Data related to Spilogale at Wikispecies
- v
- t
- e
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Suborder: Caniformia
- Western hog-nosed skunk (Conepatus mesoleucus)
- Eastern hog-nosed skunk (Conepatus leuconotus)
- Striped hog-nosed skunk (Conepatus semistriatus)
- Molina's hog-nosed skunk (Conepatus chinga)
- Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk (Conepatus humboldtii)
- Sunda stink badger (Mydaus javanensis)
- Palawan stink badger (Mydaus marchei)
- Striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis)
- Hooded skunk (Mephitis macroura)
- Western spotted skunk (Spilogale gracilis)
- Eastern spotted skunk (Spilogale putorius)
- Pygmy spotted skunk (Spilogale pygmaea)















