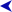
RV Calypso
 The research vessel Calypso of Jacques Cousteau arriving in Montreal on 30 August 1980 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | |
| Name | HMS J-826 |
| Builder | Ballard Marine Railway Company, Seattle, Washington, United States |
| Laid down | 12 August 1941 |
| Launched | 21 March 1942 |
| Commissioned | February 1943 |
| Recommissioned | BYMS-2026 (1944) |
| Decommissioned | 1946 |
| Renamed | Calypso G (1949) |
 France France | |
| Owner | Thomas Guinness |
| Operator | Compagnie Océanographique Française, Nice |
| Renamed | Calypso (1950) |
| Reclassified | Research vessel |
| Refit | For Cousteau (1951) |
| Fate | Sunk and raised (1996) |
| Status | Being refurbished under the direction of the Cousteau Society |
| General characteristics [1] | |
| Tonnage | 294 GRT |
| Displacement | 360 tons |
| Length | 139 ft (42 m) (43 meters, according to another source)[2] |
| Beam | 25 ft (7.6 m) |
| Draft | 10 ft (3.0 m) |
| Decks | Three |
| Installed power | 2 × 580 hp (430 kW) 8-cylinder General Motors diesel engines |
| Propulsion | Twin screw |
| Speed | 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Crew | 27 in captain's quarters, 6 staterooms and crew quarters |
| Notes |
|
RV Calypso is a former British Royal Navy minesweeper converted into a research vessel for the oceanographic researcher Jacques Cousteau, equipped with a mobile laboratory for underwater field research. She was severely damaged in 1996 and was planned to undergo a complete refurbishment in 2009–2011 that has not been accomplished. The ship is named after the Greek mythological figure Calypso.
World War II British minesweeper (1941–1947)
Calypso was originally a minesweeper built by the Ballard Marine Railway Company of Seattle, Washington, United States for the United States Navy for loan to the British Royal Navy under lend-lease. A wooden-hulled vessel, she is built of Oregon pine.[3]
She was a British yard minesweeper (BYMS) Mark 1 class motor minesweeper, laid down on 12 August 1941 with yard designation BYMS-26 and launched on 21 March 1942. She was commissioned into the Royal Navy in February 1943 as HMS J-826 and assigned to active service in the Mediterranean Sea, based in Malta, and was reclassified as BYMS-2026 in 1944. Following the end of World War II, she was decommissioned in July 1946 and laid up at Malta. On 1 August 1947 she was formally handed back to the US Navy and then struck from the US Naval Register, remaining in lay-up.[4]
Maltese ferry (1949–1950)
In May 1949 she was bought by Joseph Gasan of Malta, who had secured the mail contract on the ferry route between Marfa, in the north of Malta, and Mġarr, Gozo in 1947.[4] She was converted to a ferry and renamed Calypso G after the nymph Calypso, whose island of Ogygia was mythically associated with Gozo, entering service in March 1950. After only four months on the route, Gasan received an attractive offer and sold her.[4]
Jacques Cousteau's Calypso (1950–1997)

The British millionaire and former Member of Parliament (MP), Thomas Loel Guinness bought Calypso in July 1950.[5][6] He leased her to Cousteau for a symbolic one franc a year. He had two conditions: that Cousteau never ask him for money and that he never reveal his identity, which only came out after Cousteau's death. Cousteau restructured and transformed the ship into an expedition vessel and support base for diving, filming and oceanographic research. One of the more unusual expeditions involving the vessel was a survey of Abu Dhabi waters conducted by Cousteau on behalf of British Petroleum (BP) in 1954 – the first and last time it was used for an oil survey.[7]
Calypso carried advanced equipment, including one- and two-man mini submarines developed by Cousteau, diving saucers, and underwater scooters. The ship was also fitted with a see-through "nose" and an observation chamber 3 metres (9.8 ft) below the waterline, and was modified to house scientific equipment and a helicopter pad. The Calypso underwater camera is named after this ship.
On 8 January 1996, a barge accidentally rammed Calypso and sank her in the port of Singapore. On 16 January, she was raised by a 230-foot (70 m) crane, patched, and pumped dry before being put in a shipyard.[8]
Restoration (1997–present)


Calypso was later towed to the Maritime Museum of La Rochelle in 1998 to be an exhibit.
A legal dispute between Jacques Cousteau's widow, Francine Cousteau, and Loel Guinness, the grandson of the original owner, delayed restoration work. During this time the city of La Rochelle withdrew its funding for the restoration. Calypso remained in disrepair.[3]
In 2002, Alexandra Cousteau, Cousteau's granddaughter from his first marriage, tried to become involved in the restoration. The Cousteau Society, controlled by Francine Cousteau, reportedly spent hundreds of thousands of dollars to defend Francine's exclusive use of the name and to prevent Alexandra's participation in the restoration of Calypso.[citation needed]
In 2006 Loel Guinness transferred ownership of Calypso to the Cousteau Society for the sum of one euro. In October 2007 the ship was moved to Concarneau where restoration[clarify] began at the Piriou Shipyard.[9] Work on Calypso stopped in 2009 because of the non-payment of bills by Francine Cousteau.[10] Piriou claimed to be owed €850,000 for work already done. The Cousteau Society counter-sued for defective work. In 2015 a French court ordered Francine Cousteau to settle outstanding yard bills and remove Calypso from a Brittany shipyard or allow the shipyard to sell the vessel.[11]
The Cousteau Society announced in 2016 that a solution had been found to allow the ship to return to service with new engines.[12] In 2017 a fire damaged new wooden parts of the Calypso at a shipyard near Istanbul, Turkey, where her refitting had been in progress.[13]
Calypso in popular culture
- Calypso was the main ship in all three feature documentary films that Cousteau directed in his career: The Silent World (1956, awarded with the Academy Award for Documentary Feature and the 1956 Palme d'Or), World Without Sun (1964, which also won the Academy Award for Documentary Feature) and Voyage to the Edge of the World (1976).
- John Denver wrote a 1975 hit song "Calypso" as a tribute to Calypso and her crew. Additionally, he gave all the royalties for the song to the Cousteau Society.
- Jean Michel Jarre wrote a three part composition in tribute to the ship included on the album Waiting for Cousteau (1990).
- American heavy metal band GWAR wrote a song entitled "Je M'Appelle J. Cousteau", which was featured on their album Hell-O, originally released in 1988. It is not entirely clear whether this song is in tribute or slander, but the song is entirely about Jacques Cousteau and his ship Calypso.
- The Captain's yacht of the USS Enterprise-D, on Star Trek: The Next Generation, was named Calypso by actor Patrick Stewart. He also gave the name Cousteau to the captain's yacht of the USS Enterprise-E in homage to the Calypso's famous former captain.
- Wes Anderson directed a film homage of Jacques Cousteau's life called The Life Aquatic with Steve Zissou. In the movie, Zissou travels the seas in a ship called Belafonte. This is an oblique reference to Jacques Cousteau's ship Calypso. Harry Belafonte is a noted musician who is arguably the best known exponent of calypso music; his 1956 album Calypso is the first LP record to sell one million copies. While in the film, Belafonte is described as a "long-range sub-hunter", like Calypso she was also a former British minesweeper, the Ton-class HMS Packington.
- NASA astronaut Sunita Williams bestowed the name Calypso on the third Boeing Starliner space capsule built for the Commercial Crew Program after the ship.[14]
- The character Rebecca from the television series Theodore Tugboat is based on Calypso.
See also
- Alcyone for Cousteau's experimental turbosail ship.
- Boeing Starliner Calypso, Boeing Starliner space capsule
- HMS Calypso for the Royal Navy ships of the same name.
- SP-350 Denise first diving saucer
- Wild Goose, a private yacht belonging to John Wayne, formerly YMS-328, a sistership of Calypso.
- YMS-1-class minesweeper of the U.S. Navy, of which the BYMS was a subclass.
References
- ^ "Sea Sabres: The Calypso: The stories she could tell!". 23 July 2003. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Une pétition pour "sauver" la Calypso du commandant Cousteau". Le Point (in French). Agence France Presse. 7 October 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- ^ a b Henley, Jon (28 July 2003). "Cousteau family row may sink his ark; Watery grave awaits famous vessel in dispute over its future". The Guardian. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- ^ a b c Somner, Graeme (1982). Ferry Malta. Kendal: World Ship Society. pp. 11–12, 31. ISBN 0-905617-19-3.
- ^ Olmstead, Kathleen (2008). Jacques Cousteau: A Life Under the Sea. Sterling Publishing Company. ISBN 9781402760587.
- ^ "Le nouvel Economiste" (in French). 1996.
- ^ Morton, Michael Quentin (June 2015). "Calypso in the Arabian Gulf: Jacques Cousteau's Undersea Survey of 1954". Liwa. 5 (9): 3–28. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ "Cousteau's Calypso rescued in Singapore". CNN. 25 January 1996. Archived from the original on 1 September 2000. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- ^ "La Calypso a quitté La Rochelle jeudi matin pour être restaurée à Concarneau". Le Monde (in French). 11 October 2007. Archived from the original on 29 November 2013.
- ^ Mesgouez, Dominique (2 February 2010). "La Calypso de Cousteau dans une mauvaise passe" (in French). Ouest France. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- ^ "French shipyard threatens to sell Jacques Cousteau's boat". The Guardian. 12 March 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ^ "Calypso set to sail again!". Cousteau Society. Archived from the original on 7 January 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ "Fire on Cousteau's Calypso". www.cousteau.org. Archived from the original on 23 October 2018.
- ^ Dunbar, Brian (22 December 2019). "Starliner Returns to Earth With a New Name: Calypso". NASA.
External links

- Calypso page from the Cousteau Society.
- BYMS-26
- WWII Construction Records Yard Minesweepers (YMS)
- Miquel Pontes – "El Calypso: Historia de un mito" in Aquanet 67, 2005 [1] (.PDF file)
- Chantiers Piriou, restoration of the Calypso
- Passion Calypso, including history and photos of the ship's restoration (in French)
- Update regarding Calypso's refitting
- v
- t
- e
- 8 Jan: Calypso
- 18 Jan: North Cape, Scandia
- 27 Jan: Pacesetter
- 25 Mar: Bom Re
- 21 May: Bukoba
- 18 Sep: Sang-O-class submarine
- September (unknown date): HMFS Kiro
- November (unknown date): Lene Marie
- 9 Dec: Alexandria
- 25–26 Dec: F174
- 16 Jan: Avrasya (hostage crisis)
- 15 Feb: Sea Empress (oil spill)
- 17 May: USS Jacksonville
- June (unknown date): USS Deyo, USNS Gilliland, USS Tucson
- 29 Aug Hanseatic
- 14 Dec: Bright Field