| ARID3B |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ARID3B, BDP, DRIL2, AT-rich interaction domain 3B |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 612457; MGI: 1930768; HomoloGene: 4721; GeneCards: ARID3B; OMA:ARID3B - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 15 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 15q24.1 | Start | 74,541,206 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 74,598,131 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 9 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 9|9 B | Start | 57,697,636 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 57,744,076 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - oocyte
- gonad
- blood
- left testis
- granulocyte
- right testis
- secondary oocyte
- testicle
- bone marrow cells
- placenta
|
| | Top expressed in | - tail of embryo
- epiblast
- granulocyte
- genital tubercle
- Rostral migratory stream
- yolk sac
- zygote
- neural layer of retina
- embryo
- lens
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 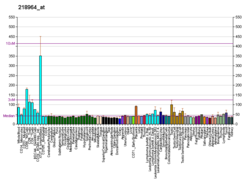 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- protein binding
- RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
| | Cellular component | | | Biological process | - regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- biological process
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 15: 74.54 – 74.6 Mb | Chr 9: 57.7 – 57.74 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
















