Protein found in humans
| PBX1 |
|---|
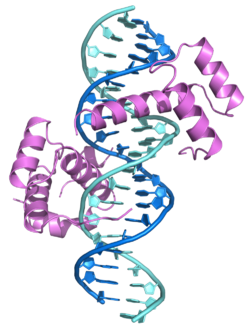 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1B72, 1PUF |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PBX1, PBX homeobox 1, CAKUHED |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 176310; MGI: 97495; HomoloGene: 20574; GeneCards: PBX1; OMA:PBX1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1q23.3 | Start | 164,555,584 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 164,899,296 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 1 H2.3|1 75.95 cM | Start | 167,946,933 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 168,259,839 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - ganglionic eminence
- optic nerve
- myometrium
- canal of the cervix
- seminal vesicula
- Brodmann area 23
- nipple
- parietal pleura
- left uterine tube
- right uterine tube
|
| | Top expressed in | - habenula
- vas deferens
- olfactory bulb
- external carotid artery
- median eminence
- ventral tegmental area
- internal carotid artery
- ciliary body
- lacrimal gland
- subiculum
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - sequence-specific DNA binding
- RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- protein heterodimerization activity
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- transcription factor binding
- protein binding
- RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- nucleus
- transcription regulator complex
- nucleoplasm
- RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex
| | Biological process | - anterior/posterior pattern specification
- proximal/distal pattern formation
- positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle
- embryonic organ development
- embryonic hemopoiesis
- negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- transcription, DNA-templated
- sex differentiation
- multicellular organism development
- embryonic limb morphogenesis
- somatic stem cell population maintenance
- regulation of cell population proliferation
- adrenal gland development
- spleen development
- thymus development
- positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- urogenital system development
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of ossification
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- negative regulation of neuron differentiation
- embryonic skeletal system development
- branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis
- steroid biosynthetic process
- cell differentiation
- animal organ morphogenesis
- positive regulation of transcription of Notch receptor target
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001204961
NM_001204963
NM_002585
NM_001353130
NM_001353131 |
| |
|---|
NM_001291508
NM_001291509
NM_008783
NM_183355 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001191890
NP_001191892
NP_002576
NP_001340059
NP_001340060 |
| |
|---|
NP_001278437
NP_001278438
NP_032809
NP_899198 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 164.56 – 164.9 Mb | Chr 1: 167.95 – 168.26 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PBX1 gene.[5] The homologous protein in Drosophila is known as extradenticle, and causes changes in embryonic development.
Function
Mice studies suggest PBX1 is involved in bone generation and skeletal patterning.[6]
Interactions
PBX1 has been shown to interact with:
Fruit fly homolog
The Drosophila melangoster gene called extradenticle encodes a homeodomain protein that is 71% similar to the Pbx1 protein, and is considered homologous to PBX1.[14] extradenticle is a homeodomain transcription factor[15] expressed during embryogenesis and is related to morphological changes and development.[14]
Reduced levels of extradenticle cause segmental transformations, without affecting the functionality or location of homeotic genes. Complete removal of extradenticle both maternally and zygotically leads to alterations from failure of non-extradenticle protein expression.[16]
A monoclonal antibody study of the expression of extradenticle protein in embryonic development found that it is uniformly distributed, as well as excluded from cell nuclei, until gastrulation. During the germ band retraction stage of development, extradenticle protein begins to accumulate in the nuclei of cells in a specific pattern. Proximal areas of wing and leg imaginal discs have extradenticle present in the nucleus, while distal areas only have it in the cytoplasm.[17]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000185630 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052534 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PBX1 Pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox 1".
- ^ "PBX1 PBX homeobox 1 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2023-06-11.
- ^ Berthelsen J, Zappavigna V, Ferretti E, Mavilio F, Blasi F (Mar 1998). "The novel homeoprotein Prep1 modulates Pbx-Hox protein cooperativity". The EMBO Journal. 17 (5): 1434–45. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.5.1434. PMC 1170491. PMID 9482740.
- ^ Piper DE, Batchelor AH, Chang CP, Cleary ML, Wolberger C (Feb 1999). "Structure of a HoxB1-Pbx1 heterodimer bound to DNA: role of the hexapeptide and a fourth homeodomain helix in complex formation". Cell. 96 (4): 587–97. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80662-5. PMID 10052460. S2CID 16122785.
- ^ Chang CP, Shen WF, Rozenfeld S, Lawrence HJ, Largman C, Cleary ML (Mar 1995). "Pbx proteins display hexapeptide-dependent cooperative DNA binding with a subset of Hox proteins". Genes & Development. 9 (6): 663–74. doi:10.1101/gad.9.6.663. PMID 7729685.
- ^ Shen WF, Rozenfeld S, Kwong A, Köm ves LG, Lawrence HJ, Largman C (Apr 1999). "HOXA9 forms triple complexes with PBX2 and MEIS1 in myeloid cells". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (4): 3051–61. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.4.3051. PMC 84099. PMID 10082572.
- ^ Shanmugam K, Green NC, Rambaldi I, Saragovi HU, Featherstone MS (Nov 1999). "PBX and MEIS as non-DNA-binding partners in trimeric complexes with HOX proteins". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (11): 7577–88. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.11.7577. PMC 84774. PMID 10523646.
- ^ Jacobs Y, Schnabel CA, Cleary ML (Jul 1999). "Trimeric association of Hox and TALE homeodomain proteins mediates Hoxb2 hindbrain enhancer activity". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (7): 5134–42. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.7.5134. PMC 84356. PMID 10373562.
- ^ Zubair M, Ishihara S, Oka S, Okumura K, Morohashi K (Jun 2006). "Two-step regulation of Ad4BP/SF-1 gene transcription during fetal adrenal development: initiation by a Hox-Pbx1-Prep1 complex and maintenance via autoregulation by Ad4BP/SF-1". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 26 (11): 4111–21. doi:10.1128/MCB.00222-06. PMC 1489093. PMID 16705164.
- ^ a b Rauskolb C, Peifer M, Wieschaus E (September 1993). "extradenticle, a regulator of homeotic gene activity, is a homolog of the homeobox-containing human proto-oncogene pbx1". Cell. 74 (6): 1101–1112. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90731-5. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 8104703. S2CID 44721382.
- ^ Aspland S, White R (1997-02-01). "Nucleocytoplasmic localisation of extradenticle protein is spatially regulated throughout development in Drosophila". Development. 124 (3): 741–747. doi:10.1242/dev.124.3.741. ISSN 1477-9129. PMID 9043089.
- ^ Peifer M, Wieschaus E (1990-07-01). "Mutations in the Drosophila gene extradenticle affect the way specific homeo domain proteins regulate segmental identity". Genes & Development. 4 (7): 1209–1223. doi:10.1101/gad.4.7.1209. ISSN 0890-9369. PMID 1976570.
- ^ "Nucleocytoplasmic localisation of extradenticle protein is spatially regulated throughout development in Drosophila". journals.biologists.com. Retrieved 2023-06-06.
Further reading
- Sanyal M, Tung JW, Karsunky H, Zeng H, Selleri L, Weissman IL, Herzenberg LA, Cleary ML (May 2007). "B-cell development fails in the absence of the Pbx1 proto-oncogene". Blood. 109 (10): 4191–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-054213. PMC 1885499. PMID 17244677.
- Hui H, Perfetti R (Feb 2002). "Pancreas duodenum homeobox-1 regulates pancreas development during embryogenesis and islet cell function in adulthood". European Journal of Endocrinology. 146 (2): 129–41. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1460129. PMID 11834421.
- Hunger SP, Galili N, Carroll AJ, Crist WM, Link MP, Cleary ML (Feb 1991). "The t(1;19)(q23;p13) results in consistent fusion of E2A and PBX1 coding sequences in acute lymphoblastic leukemias". Blood. 77 (4): 687–93. doi:10.1182/blood.V77.4.687.687. PMID 1671560.
- Monica K, Galili N, Nourse J, Saltman D, Cleary ML (Dec 1991). "PBX2 and PBX3, new homeobox genes with extensive homology to the human proto-oncogene PBX1". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 11 (12): 6149–57. doi:10.1128/mcb.11.12.6149. PMC 361792. PMID 1682799.
- Nourse J, Mellentin JD, Galili N, Wilkinson J, Stanbridge E, Smith SD, Cleary ML (Feb 1990). "Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor". Cell. 60 (4): 535–45. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90657-Z. PMID 1967982. S2CID 7975269.
- Kamps MP, Murre C, Sun XH, Baltimore D (Feb 1990). "A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL". Cell. 60 (4): 547–55. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. PMID 1967983. S2CID 39661371.
- Lu Q, Wright DD, Kamps MP (Jun 1994). "Fusion with E2A converts the Pbx1 homeodomain protein into a constitutive transcriptional activator in human leukemias carrying the t(1;19) translocation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 14 (6): 3938–48. doi:10.1128/mcb.14.6.3938. PMC 358760. PMID 7910944.
- Van Dijk MA, Voorhoeve PM, Murre C (Jul 1993). "Pbx1 is converted into a transcriptional activator upon acquiring the N-terminal region of E2A in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastoid leukemia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (13): 6061–5. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.6061D. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.13.6061. PMC 46867. PMID 8327485.
- Lu Q, Kamps MP (Apr 1996). "Structural determinants within Pbx1 that mediate cooperative DNA binding with pentapeptide-containing Hox proteins: proposal for a model of a Pbx1-Hox-DNA complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 16 (4): 1632–40. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.4.1632. PMC 231149. PMID 8657138.
- Berthelsen J, Zappavigna V, Mavilio F, Blasi F (Mar 1998). "Prep1, a novel functional partner of Pbx proteins". The EMBO Journal. 17 (5): 1423–33. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.5.1423. PMC 1170490. PMID 9482739.
- Berthelsen J, Zappavigna V, Ferretti E, Mavilio F, Blasi F (Mar 1998). "The novel homeoprotein Prep1 modulates Pbx-Hox protein cooperativity". The EMBO Journal. 17 (5): 1434–45. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.5.1434. PMC 1170491. PMID 9482740.
- Piper DE, Batchelor AH, Chang CP, Cleary ML, Wolberger C (Feb 1999). "Structure of a HoxB1-Pbx1 heterodimer bound to DNA: role of the hexapeptide and a fourth homeodomain helix in complex formation". Cell. 96 (4): 587–97. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80662-5. PMID 10052460. S2CID 16122785.
- Shen WF, Rozenfeld S, Kwong A, Köm ves LG, Lawrence HJ, Largman C (Apr 1999). "HOXA9 forms triple complexes with PBX2 and MEIS1 in myeloid cells". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (4): 3051–61. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.4.3051. PMC 84099. PMID 10082572.
- Jacobs Y, Schnabel CA, Cleary ML (Jul 1999). "Trimeric association of Hox and TALE homeodomain proteins mediates Hoxb2 hindbrain enhancer activity". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (7): 5134–42. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.7.5134. PMC 84356. PMID 10373562.
- Knoepfler PS, Bergstrom DA, Uetsuki T, Dac-Korytko I, Sun YH, Wright WE, Tapscott SJ, Kamps MP (Sep 1999). "A conserved motif N-terminal to the DNA-binding domains of myogenic bHLH transcription factors mediates cooperative DNA binding with pbx-Meis1/Prep1". Nucleic Acids Research. 27 (18): 3752–61. doi:10.1093/nar/27.18.3752. PMC 148632. PMID 10471746.
- McWhirter JR, Neuteboom ST, Wancewicz EV, Monia BP, Downing JR, Murre C (Sep 1999). "Oncogenic homeodomain transcription factor E2A-Pbx1 activates a novel WNT gene in pre-B acute lymphoblastoid leukemia". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (20): 11464–9. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9611464M. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.20.11464. PMC 18056. PMID 10500199.
- Shanmugam K, Green NC, Rambaldi I, Saragovi HU, Featherstone MS (Nov 1999). "PBX and MEIS as non-DNA-binding partners in trimeric complexes with HOX proteins". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (11): 7577–88. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.11.7577. PMC 84774. PMID 10523646.
- Mikkola I, Bruun JA, Holm T, Johansen T (Feb 2001). "Superactivation of Pax6-mediated transactivation from paired domain-binding sites by dna-independent recruitment of different homeodomain proteins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (6): 4109–18. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008882200. PMID 11069920.
- Thameem F, Wolford JK, Bogardus C, Prochazka M (Mar 2001). "Analysis of PBX1 as a candidate gene for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1518 (1–2): 215–20. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(01)00189-0. PMID 11267683.
- Liu Y, MacDonald RJ, Swift GH (May 2001). "DNA binding and transcriptional activation by a PDX1.PBX1b.MEIS2b trimer and cooperation with a pancreas-specific basic helix-loop-helix complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (21): 17985–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100678200. PMID 11279116.
- Mal A, Sturniolo M, Schiltz RL, Ghosh MK, Harter ML (Apr 2001). "A role for histone deacetylase HDAC1 in modulating the transcriptional activity of MyoD: inhibition of the myogenic program". The EMBO Journal. 20 (7): 1739–53. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.7.1739. PMC 145490. PMID 11285237.
External links
- PBX1+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P40424 (Human Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1) at the PDBe-KB.
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P41778 (Mouse Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1) at the PDBe-KB.
PDB gallery
-
1b72: PBX1, HOMEOBOX PROTEIN HOX-B1/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX -
1b8i: STRUCTURE OF THE HOMEOTIC UBX/EXD/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX -
1du6: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE TRUNCATED PBX HOMEODOMAIN -
1lfu: NMR solution structure of the extended PBX homeodomain bound to DNA -
1puf: Crystal structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNA |
|
|---|
(1) Basic domains |
|---|
| (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) | |
|---|
| (1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) | | Group A | |
|---|
| Group B | |
|---|
Group C
bHLH-PAS | |
|---|
| Group D | |
|---|
| Group E | |
|---|
Group F
bHLH-COE | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (1.3) bHLH-ZIP | |
|---|
| (1.4) NF-1 | |
|---|
| (1.5) RF-X | |
|---|
| (1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH) | |
|---|
|
|
(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains |
|---|
| (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4) | | subfamily 1 | |
|---|
| subfamily 2 | |
|---|
| subfamily 3 | |
|---|
| subfamily 4 | |
|---|
| subfamily 5 | |
|---|
| subfamily 6 | |
|---|
| subfamily 0 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| (2.2) Other Cys4 | |
|---|
| (2.3) Cys2His2 | |
|---|
| (2.4) Cys6 | |
|---|
| (2.5) Alternating composition | |
|---|
| (2.6) WRKY | |
|---|
|
|
|
(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts |
|---|
|
|
(0) Other transcription factors |
|---|
|
|
see also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies |

 1b72: PBX1, HOMEOBOX PROTEIN HOX-B1/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX
1b72: PBX1, HOMEOBOX PROTEIN HOX-B1/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX 1b8i: STRUCTURE OF THE HOMEOTIC UBX/EXD/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX
1b8i: STRUCTURE OF THE HOMEOTIC UBX/EXD/DNA TERNARY COMPLEX 1du6: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE TRUNCATED PBX HOMEODOMAIN
1du6: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE TRUNCATED PBX HOMEODOMAIN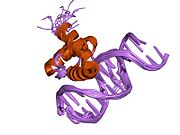 1lfu: NMR solution structure of the extended PBX homeodomain bound to DNA
1lfu: NMR solution structure of the extended PBX homeodomain bound to DNA 1puf: Crystal structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNA
1puf: Crystal structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 homeodomains bound to DNA























