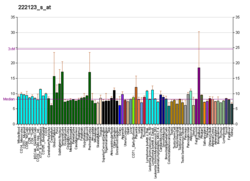
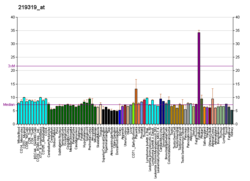
HIF3A
| HIF3A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | HIF3A, HIF-3A, IPAS, MOP7, PASD7, bHLHe17, HIF3-alpha-1, hypoxia inducible factor 3 alpha subunit, hypoxia inducible factor 3 subunit alpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 609976; MGI: 1859778; HomoloGene: 9646; GeneCards: HIF3A; OMA:HIF3A - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hypoxia-inducible factor 3 alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIF3A gene.[5][6][7]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha-3 subunit of one of several alpha/beta-subunit heterodimeric transcription factors that regulate many adaptive responses to low oxygen tension (hypoxia). The alpha-3 subunit lacks the transactivation domain found in factors containing either the alpha-1 or alpha-2 subunits. It is thought that factors containing the alpha-3 subunit are negative regulators of hypoxia-inducible gene expression. At least three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
In rats, it plays a negative role in the adaptation to hypoxia, because the inhibition of HIF-3α expression leads to an increase in physical endurance.[8]
Clinical significance
DNA methylation in the introns of HIF3A is associated with BMI an adiposity.[9]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000124440 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000004328 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Hara S, Hamada J, Kobayashi C, Kondo Y, Imura N (Sep 2001). "Expression and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha in human kidney: suppression of HIF-mediated gene expression by HIF-3alpha". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 287 (4): 808–13. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5659. PMID 11573933.
- ^ Makino Y, Cao R, Svensson K, Bertilsson G, Asman M, Tanaka H, Cao Y, Berkenstam A, Poellinger L (Dec 2001). "Inhibitory PAS domain protein is a negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible gene expression". Nature. 414 (6863): 550–4. Bibcode:2001Natur.414..550M. doi:10.1038/35107085. PMID 11734856. S2CID 4389117.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: HIF3A hypoxia inducible factor 3, alpha subunit".
- ^ Drevytska T, Gavenauskas B, Drozdovska S, Nosar V, Dosenko V, Mankovska I (2012). "HIF-3α mRNA expression changes in different tissues and their role in adaptation to intermittent hypoxia and physical exercise". Pathophysiology. 19 (3): 205–14. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2012.06.002. PMID 22884965.
- ^ Dick KJ, Nelson CP, Tsaprouni L, Sandling JK, Aïssi D, Wahl S, Meduri E, Morange PE, Gagnon F, Grallert H, Waldenberger M, Peters A, Erdmann J, Hengstenberg C, Cambien F, Goodall AH, Ouwehand WH, Schunkert H, Thompson JR, Spector TD, Gieger C, Trégouët DA, Deloukas P, Samani NJ (2014). "DNA methylation and body-mass index: a genome-wide analysis". Lancet. 383 (9933): 1990–1998. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62674-4. PMID 24630777. S2CID 18026508.
Further reading
- Gu YZ, Moran SM, Hogenesch JB, Wartman L, Bradfield CA (1998). "Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of a third alpha-class hypoxia inducible factor subunit, HIF3alpha". Gene Expr. 7 (3): 205–13. PMC 6151950. PMID 9840812.
- Makino Y, Kanopka A, Wilson WJ, Tanaka H, Poellinger L (2002). "Inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS) is a hypoxia-inducible splicing variant of the hypoxia-inducible factor-3alpha locus". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (36): 32405–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200328200. PMID 12119283.
- Maynard MA, Qi H, Chung J, Lee EH, Kondo Y, Hara S, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Ohh M (2003). "Multiple splice variants of the human HIF-3 alpha locus are targets of the von Hippel-Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase complex". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (13): 11032–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208681200. PMID 12538644.
- Maynard MA, Evans AJ, Hosomi T, Hara S, Jewett MA, Ohh M (2006). "Human HIF-3alpha4 is a dominant-negative regulator of HIF-1 and is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma". FASEB J. 19 (11): 1396–406. doi:10.1096/fj.05-3788com. PMID 16126907. S2CID 86404533.
- Jang MS, Park JE, Lee JA, Park SG, Myung PK, Lee DH, Park BC, Cho S (2005). "Binding and regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by the inhibitory PAS proteins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 337 (1): 209–15. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.09.038. PMID 16182248.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R, Yamamoto J, Sekine M, Tsuritani K, Wakaguri H, Ishii S, Sugiyama T, Saito K, Isono Y, Irie R, Kushida N, Yoneyama T, Otsuka R, Kanda K, Yokoi T, Kondo H, Wagatsuma M, Murakawa K, Ishida S, Ishibashi T, Takahashi-Fujii A, Tanase T, Nagai K, Kikuchi H, Nakai K, Isogai T, Sugano S (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Li QF, Wang XR, Yang YW, Lin H (2006). "Hypoxia upregulates hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha expression in lung epithelial cells: characterization and comparison with HIF-1alpha". Cell Res. 16 (6): 548–58. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7310072. PMID 16775626.
- Kollers S, Musilova P, Rubes J, Rocha D (2007). "Comparative mapping reveals multiple rearrangements between pig chromosome 6 and human 19q13". Anim. Genet. 37 (6): 595–6. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2006.01516.x. PMID 17121608.
- v
- t
- e
(1) Basic domains | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(3) Helix-turn-helix domains | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
(0) Other transcription factors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 19 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e