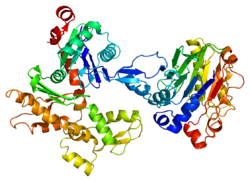
Beta-actin
| ACTB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ACTB, BRWS1, PS1TP5BP1, Beta-actin, actin, beta, actin beta | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 102630; MGI: 87904; HomoloGene: 110648; GeneCards: ACTB; OMA:ACTB - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Actin beta (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee abbreviation ACTB/ACTB) is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified in humans. This is one of the two nonmuscle cytoskeletal actins. Actins are highly conserved proteins[5][6] that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus.[7]
Interactions
Actin beta has been shown to interact with SPTBN2.[8][9] In addition, RNA-binding protein Sam68 was found to interact with the mRNA encoding actin beta, which regulates the synaptic formation of the dendritic spines with its cytoskeletal components.
Actin beta has been shown to activate eNOS, thereby increasing NO production. An eight-amino acid motif (326-333) in eNOS has been shown to mediate the interaction between actin and eNOS.[10]
Clinical relevance
Recurrent mutations in this gene have been associated to cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.[11]
Applications
Actin beta is often used in Western blotting as a loading control, to normalize total protein amounts and check for eventual protein degradation in the samples. Its transcript is also commonly used as a housekeeping gene standard in qPCR. Its molecular weight is approximately 42 kDa.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000075624 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029580 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Gunning PW, Ghoshdastider U, Whitaker S, Popp D, Robinson RC (Jun 2015). "The evolution of compositionally and functionally distinct actin filaments". Journal of Cell Science. 128 (11): 2009–2019. doi:10.1242/jcs.165563. PMID 25788699.
- ^ Hanukoglu I, Tanese N, Fuchs E (Feb 1983). "Complementary DNA sequence of a human cytoplasmic actin. Interspecies divergence of 3' non-coding regions". Journal of Molecular Biology. 163 (4): 673–8. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(83)90117-1. PMID 6842590.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ACTB actin, beta".
- ^ Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Glinka A, Niehrs C (May 2001). "LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins". Nature. 411 (6835): 321–5. Bibcode:2001Natur.411..321M. doi:10.1038/35077108. PMID 11357136. S2CID 4323027.
- ^ Holleran EA, Ligon LA, Tokito M, Stankewich MC, Morrow JS, Holzbaur EL (Sep 2001). "beta III spectrin binds to the Arp1 subunit of dynactin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (39): 36598–605. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104838200. PMID 11461920.
- ^ Kondrikov D, Fonseca FV, Elms S, Fulton D, Black SM, Block ER, Su Y (Feb 2010). "Beta-actin association with endothelial nitric-oxide synthase modulates nitric oxide and superoxide generation from the enzyme". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285 (7): 4319–27. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.063172. PMC 2836036. PMID 19946124.
- ^ Lohr JG, Stojanov P, Lawrence MS, Auclair D, Chapuy B, Sougnez C, Cruz-Gordillo P, Knoechel B, Asmann YW, Slager SL, Novak AJ, Dogan A, Ansell SM, Link BK, Zou L, Gould J, Saksena G, Stransky N, Rangel-Escareño C, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Melendez-Zajgla J, Hernández-Lemus E, Schwarz-Cruz y Celis A, Imaz-Rosshandler I, Ojesina AI, Jung J, Pedamallu CS, Lander ES, Habermann TM, Cerhan JR, Shipp MA, Getz G, Golub TR (Mar 2012). "Discovery and prioritization of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) by whole-exome sequencing". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (10): 3879–84. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.3879L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121343109. PMC 3309757. PMID 22343534.
External links
- Human ACTB genome location and ACTB gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P60709 (Actin, cytoplasmic 1) at the PDBe-KB.
Further reading
- Vandekerckhove J, Leavitt J, Kakunaga T, Weber K (1980). "Coexpression of a mutant beta-actin and the two normal beta- and gamma-cytoplasmic actins in a stably transformed human cell line". Cell. 22 (3): 893–9. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(80)90566-8. PMID 6893954. S2CID 54299848.
- Leavitt J, Gunning P, Porreca P, Ng SY, Lin CS, Kedes L (1984). "Molecular cloning and characterization of mutant and wild-type human beta-actin genes". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 4 (10): 1961–9. doi:10.1128/mcb.4.10.1961. PMC 369012. PMID 6095033.
- Ng SY, Gunning P, Eddy R, Ponte P, Leavitt J, Shows T, Kedes L (1985). "Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 5 (10): 2720–32. doi:10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. PMC 367010. PMID 3837182.
- Snásel J, Pichová I (1997). "The cleavage of host cell proteins by HIV-1 protease". Folia Biologica. 42 (5): 227–30. doi:10.1007/BF02818986. PMID 8997639. S2CID 7617882.
- Gunning P, Weinberger R, Jeffrey P (Apr 1997). "Actin and tropomyosin isoforms in morphogenesis". Anatomy and Embryology. 195 (4): 311–5. doi:10.1007/s004290050050. PMID 9108196. S2CID 9692297.
- Kimura T, Hashimoto I, Nishikawa M, Fujisawa JI (1997). "A role for Rev in the association of HIV-1 gag mRNA with cytoskeletal beta-actin and viral protein expression". Biochimie. 78 (11–12): 1075–80. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(97)86732-6. PMID 9150887.
- Szentirmay MN, Sawadogo M (May 2000). "Spatial organization of RNA polymerase II transcription in the nucleus". Nucleic Acids Research. 28 (10): 2019–25. doi:10.1093/nar/28.10.2019. PMC 105382. PMID 10773068.
- Anderson JL, Hope TJ (Apr 2004). "HIV accessory proteins and surviving the host cell". Current HIV/AIDS Reports. 1 (1): 47–53. doi:10.1007/s11904-004-0007-x. PMID 16091223. S2CID 34731265.
- Pederson T, Aebi U (Nov 2005). "Nuclear actin extends, with no contraction in sight". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 16 (11): 5055–60. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-07-0656. PMC 1266405. PMID 16148048.
- Perrin BJ, Ervasti JM (Oct 2010). "The actin gene family: function follows isoform". Cytoskeleton. 67 (10): 630–4. doi:10.1002/cm.20475. PMC 2949686. PMID 20737541.
See also
- v
- t
- e
-
 1atn: Atomic structure of the actin:DNASE I complex
1atn: Atomic structure of the actin:DNASE I complex -
 1c0f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF DICTYOSTELIUM CAATP-ACTIN IN COMPLEX WITH GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1
1c0f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF DICTYOSTELIUM CAATP-ACTIN IN COMPLEX WITH GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1 -
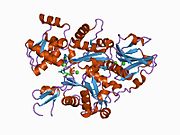 1c0g: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF 1:1 COMPLEX BETWEEN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1 AND A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 228: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/E360H)
1c0g: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF 1:1 COMPLEX BETWEEN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1 AND A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 228: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/E360H) -
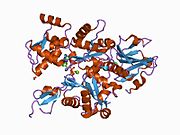 1d4x: Crystal Structure of Caenorhabditis Elegans Mg-ATP Actin Complexed with Human Gelsolin Segment 1 at 1.75 A resolution.
1d4x: Crystal Structure of Caenorhabditis Elegans Mg-ATP Actin Complexed with Human Gelsolin Segment 1 at 1.75 A resolution. -
 1dej: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 646: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/A231K/S232E/E360H) IN COMPLEX WITH HUMAN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1
1dej: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 646: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/A231K/S232E/E360H) IN COMPLEX WITH HUMAN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1 -
 1eqy: COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA-ACTIN: HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 1
1eqy: COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA-ACTIN: HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 1 -
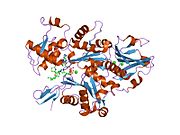 1esv: COMPLEX BETWEEN LATRUNCULIN A:RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA ACTIN:HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 1
1esv: COMPLEX BETWEEN LATRUNCULIN A:RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA ACTIN:HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 1 -
 1h1v: GELSOLIN G4-G6/ACTIN COMPLEX
1h1v: GELSOLIN G4-G6/ACTIN COMPLEX -
 1hlu: STRUCTURE OF BOVINE BETA-ACTIN-PROFILIN COMPLEX WITH ACTIN BOUND ATP PHOSPHATES SOLVENT ACCESSIBLE
1hlu: STRUCTURE OF BOVINE BETA-ACTIN-PROFILIN COMPLEX WITH ACTIN BOUND ATP PHOSPHATES SOLVENT ACCESSIBLE -
 1ijj: THE X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE ACTIN AND LATRUNCULIN A AT 2.85 A RESOLUTION
1ijj: THE X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE ACTIN AND LATRUNCULIN A AT 2.85 A RESOLUTION -
 1j6z: UNCOMPLEXED ACTIN
1j6z: UNCOMPLEXED ACTIN -
 1kxp: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN
1kxp: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN -
 1lcu: Polylysine Induces an Antiparallel Actin Dimer that Nucleates Filament Assembly: Crystal Structure at 3.5 A Resolution
1lcu: Polylysine Induces an Antiparallel Actin Dimer that Nucleates Filament Assembly: Crystal Structure at 3.5 A Resolution -
 1lot: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF ACTIN WITH VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN
1lot: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF ACTIN WITH VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN -
 1m8q: Molecular Models of Averaged Rigor Crossbridges from Tomograms of Insect Flight Muscle
1m8q: Molecular Models of Averaged Rigor Crossbridges from Tomograms of Insect Flight Muscle -
 1ma9: Crystal structure of the complex of human vitamin D binding protein and rabbit muscle actin
1ma9: Crystal structure of the complex of human vitamin D binding protein and rabbit muscle actin -
 1mdu: Crystal structure of the chicken actin trimer complexed with human gelsolin segment 1 (GS-1)
1mdu: Crystal structure of the chicken actin trimer complexed with human gelsolin segment 1 (GS-1) -
 1mvw: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1mvw: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1nlv: Crystal Structure Of Dictyostelium Discoideum Actin Complexed With Ca ATP And Human Gelsolin Segment 1
1nlv: Crystal Structure Of Dictyostelium Discoideum Actin Complexed With Ca ATP And Human Gelsolin Segment 1 -
 1nm1: Crystal Structure of D. Dicsoideum Actin Complexed With Gelsolin Segment 1 and Mg ATP at 1.8 A Resolution
1nm1: Crystal Structure of D. Dicsoideum Actin Complexed With Gelsolin Segment 1 and Mg ATP at 1.8 A Resolution -
 1nmd: Crystal Structure of D. Discoideum Actin-Gelsolin Segment 1 Complex Crystallized In Presence Of Lithium ATP
1nmd: Crystal Structure of D. Discoideum Actin-Gelsolin Segment 1 Complex Crystallized In Presence Of Lithium ATP -
 1nwk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MONOMERIC ACTIN IN THE ATP STATE
1nwk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MONOMERIC ACTIN IN THE ATP STATE -
 1o18: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o18: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o19: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o19: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1a: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1a: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1b: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1b: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1c: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1c: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1d: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1d: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1e: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1e: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1f: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1f: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1o1g: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE
1o1g: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE -
 1p8z: Complex Between Rabbit Muscle alpha-Actin: Human Gelsolin Residues Val26-Glu156
1p8z: Complex Between Rabbit Muscle alpha-Actin: Human Gelsolin Residues Val26-Glu156 -
 1qz5: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with kabiramide C
1qz5: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with kabiramide C -
 1qz6: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with jaspisamide A
1qz6: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with jaspisamide A -
 1rdw: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer
1rdw: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer -
 1rfq: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer
1rfq: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer -
 1rgi: Crystal structure of gelsolin domains G1-G3 bound to actin
1rgi: Crystal structure of gelsolin domains G1-G3 bound to actin -
 1s22: Absolute Stereochemistry of Ulapualide A
1s22: Absolute Stereochemistry of Ulapualide A -
 1sqk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CIBOULOT IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN
1sqk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CIBOULOT IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN -
 1t44: Structural basis of actin sequestration by thymosin-B4: Implications for arp2/3 activation
1t44: Structural basis of actin sequestration by thymosin-B4: Implications for arp2/3 activation -
 1wua: The structure of Aplyronine A-actin complex
1wua: The structure of Aplyronine A-actin complex -
 1y64: Bni1p Formin Homology 2 Domain complexed with ATP-actin
1y64: Bni1p Formin Homology 2 Domain complexed with ATP-actin -
 1yxq: Crystal structure of actin in complex with swinholide A
1yxq: Crystal structure of actin in complex with swinholide A -
 2a3z: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WASP with Actin-DNAse I
2a3z: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WASP with Actin-DNAse I -
 2a40: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WAVE with Actin-DNAse I
2a40: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WAVE with Actin-DNAse I -
 2a41: Ternary complex of the WH2 Domain of WIP with Actin-DNAse I
2a41: Ternary complex of the WH2 Domain of WIP with Actin-DNAse I -
 2a42: Actin-DNAse I Complex
2a42: Actin-DNAse I Complex -
 2a5x: Crystal Structure of a Cross-linked Actin Dimer
2a5x: Crystal Structure of a Cross-linked Actin Dimer -
 2asm: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide A
2asm: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide A -
 2aso: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Sphinxolide B
2aso: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Sphinxolide B -
 2asp: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide C
2asp: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide C -
 2btf: THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE PROFILIN-BETA-ACTIN
2btf: THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE PROFILIN-BETA-ACTIN -
 2d1k: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of mim with actin-dnase I
2d1k: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of mim with actin-dnase I -
 2ff3: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:N-wasp V2 motif hybrid in complex with actin
2ff3: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:N-wasp V2 motif hybrid in complex with actin -
 2ff6: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:ciboulot domain 2 hybrid in complex with actin
2ff6: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:ciboulot domain 2 hybrid in complex with actin -
 2fxu: X-ray Structure of Bistramide A- Actin Complex at 1.35 A resolution.
2fxu: X-ray Structure of Bistramide A- Actin Complex at 1.35 A resolution. -
 2gwj: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: hexagonal crystal form
2gwj: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: hexagonal crystal form -
 2gwk: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: orthorhombic crystal form
2gwk: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: orthorhombic crystal form -
 2hf3: Crystal structure of monomeric Actin in the ADP bound state
2hf3: Crystal structure of monomeric Actin in the ADP bound state -
 2hf4: Crystal structure of Monomeric Actin in its ATP-bound state
2hf4: Crystal structure of Monomeric Actin in its ATP-bound state -
 2hmp: Uncomplexed actin cleaved with protease ECP32
2hmp: Uncomplexed actin cleaved with protease ECP32 -
 2oan: Structure of oxidized beta-actin
2oan: Structure of oxidized beta-actin -
 2q1n: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 374
2q1n: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 374 -
 2q31: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 374 and proteolytically cleaved by subtilisin between residues 47 and 48.
2q31: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 374 and proteolytically cleaved by subtilisin between residues 47 and 48. -
 2q36: Actin Dimer Cross-linked between Residues 191 and 374 and complexed with Kabiramide C
2q36: Actin Dimer Cross-linked between Residues 191 and 374 and complexed with Kabiramide C
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 7 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e



















































































